The consortium of the ITEA project Familiar has developed an architecture for federated machine learning (FedML) with head-mounted mixed-reality (XR) displays and analyzed it in use cases. In one of the application scenarios, the consortium leader consider it and the partners Fraunhofer Research Institution for Additive Manufacturing Technologies IAPT, NXRT, and Pumacy Technologies developed a digital assistance system for setting up robotic DED-Arc.
Familiar: Safe and efficient machine learning
The Familiar project aims to optimize workflows and increase efficiency in manufacturing companies through machine learning (ML). Collaborative learning between edge devices and decentralized data storage ensures data security and opens up the advantages of machine learning as well as virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR) to sensitive industries. Use cases from the automotive industry and additive manufacturing (AM) served for analysis and validation in the project.
In a sub-project of the ITEA project Familiar, Fraunhofer IAPT worked with project partners on a setup assistance for robotic DED-Arc. The Fraunhofer IAPT focused on developing the system architecture in the 3D printing facility, integrating sensors, developing data streams and interfaces, as well as evaluations and tests.

Challenges of robotic DED-Arc
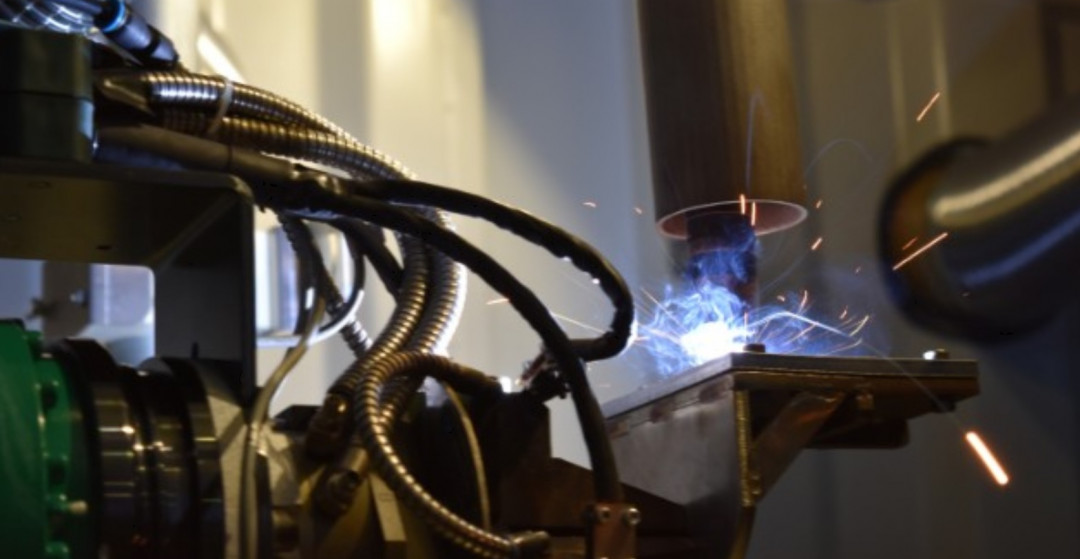
DED-Arc (often referred to as WAAM – Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing) is part of the Directed Energy Deposition (DED) processes. The additive manufacturing technology builds components layer by layer by melting metal wire through an arc. The advantages of DED-Arc over other 3D printing methods include high speed and efficient material usage. DED-Arc produces large structures faster and more cost-effectively than powder processes. Additionally, the components are characterized by high strength and favorable mechanical properties.
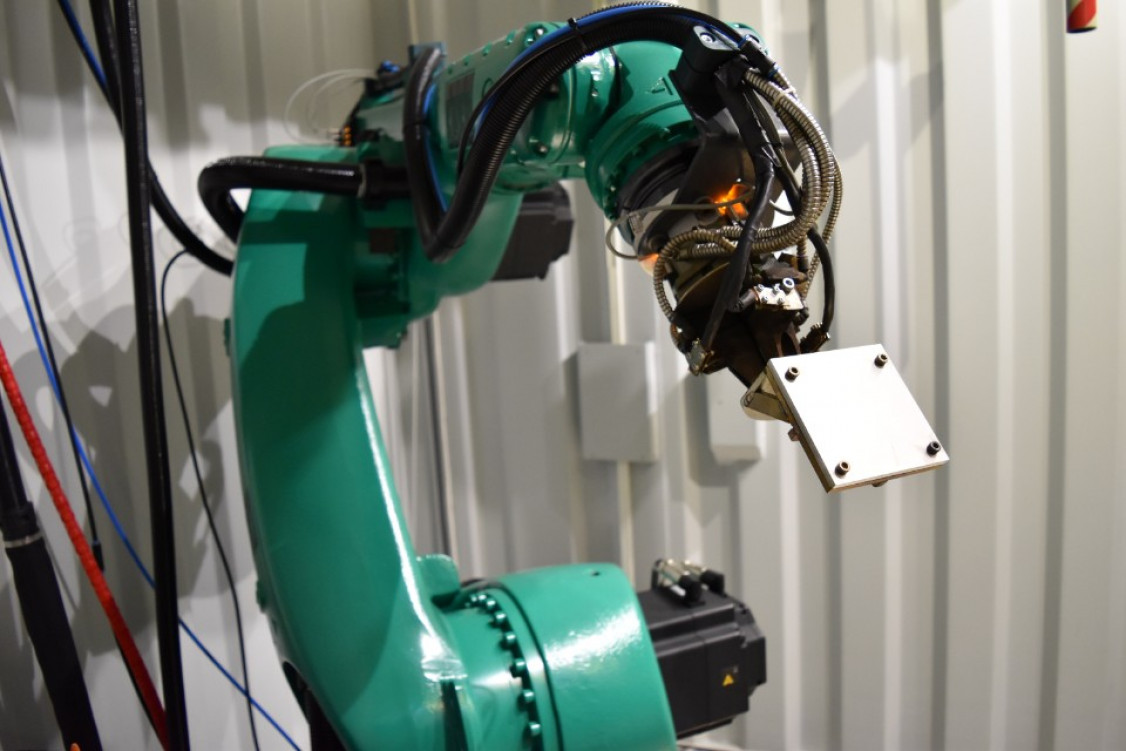
However, robotic DED-Arc is complex and requires extensive knowledge of production processes. The setup of the robotic 3D printing process determines the quality of the process and the components. For example, insufficient clamping of the metallic substrate plates can lead to deformation of the substrate plate and costly rework or scrap production.
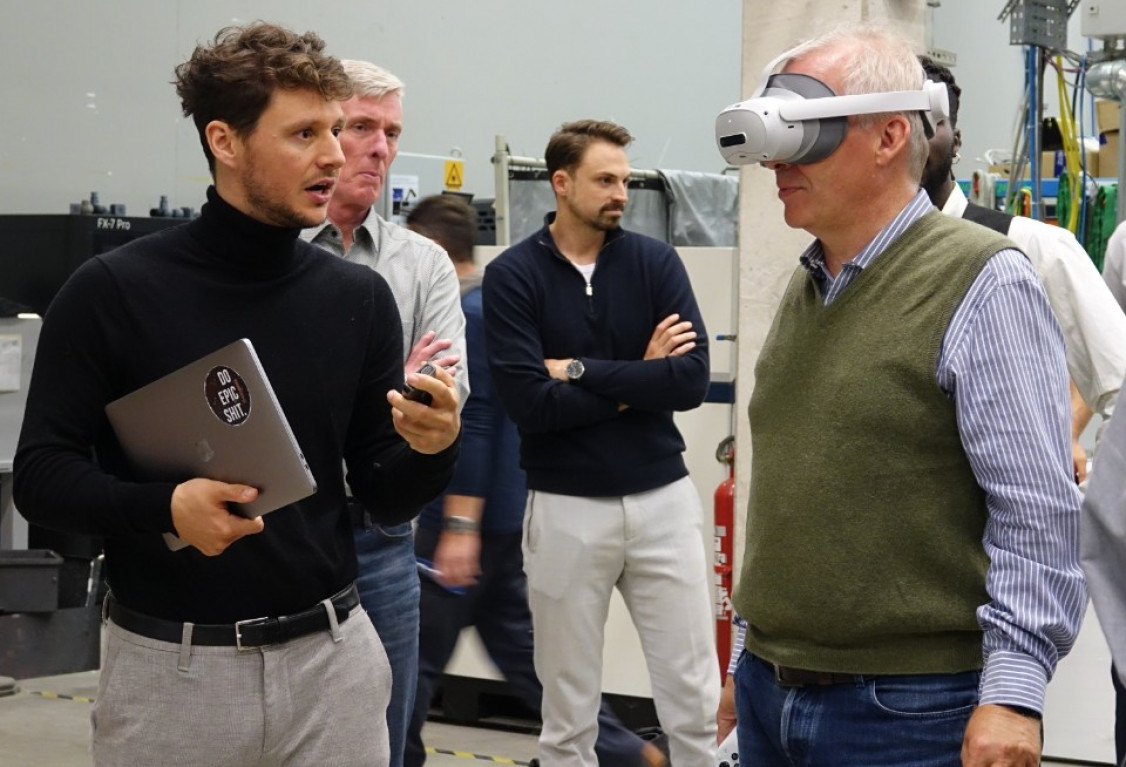

Digital assistance system: Quick and safe set up of DED-Arc processes
The new assistance system guides operators through the setup of the robotic 3D printing process using mixed-reality (XR) glasses. Sensor data from an in-process stereo camera trains the machine learning model that calculates the setup parameters for robotic DED-Arc.
The resulting digital assistance system eliminates inefficient process steps and reduces the preparation effort for DED-Arc production by half. Beyond the time savings in the preparation of additive manufacturing, the assistance system contributes to improving the quality of DED-Arc components.
About Familiar
ITEA is a Eureka cluster for software innovations that support European companies in digitalization. The 3-year ITEA project Familiar (Holistic Federated AI Development for Mixed-Reality Applications in Europe) involved project partners from Germany, Turkey and Austria. The application case for additive manufacturing was funded by the Federal Ministry for Research, Technology, and Space (BMFTR) and the Austrian Research Promotion Agency FFG.
(Source: Fraunhofer IAPT)
Schlagworte
ARAugmented RealityAutomotiveDED-ArcDirect Energy DepositionLaserMRRobotVirtual RealityVRWAAMWeldingWire Arc Additive Manufacturing






