
Recycling the non-recyclable: New epoxy resin resists flames and reduces waste
Empa researchers have developed an epoxy resin that can be repaired and recycled, in addition to being flame-retardant and mechanically strong. Potential applications range from coating for wooden flooring to composites in aerospace and railways.
Epoxy resins are tough and versatile polymers. In combination with glass or carbon fibers, they are used, for example, to manufacture components for aircraft, cars, trains, ships and wind turbines. Such epoxy-based fiber-reinforced polymers have excellent mechanical and thermal properties and are much lighter than metal. Their weakness: They are not recyclable – at least not yet.
Now Empa researchers led by Sabyasachi Gaan at Empa's Advanced Fibers laboratory have developed an epoxy resin-based plastic that is fully recyclable, repairable and also flame retardant – all while retaining the favorable thermomechanical properties of epoxy resins. They have published their findings in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
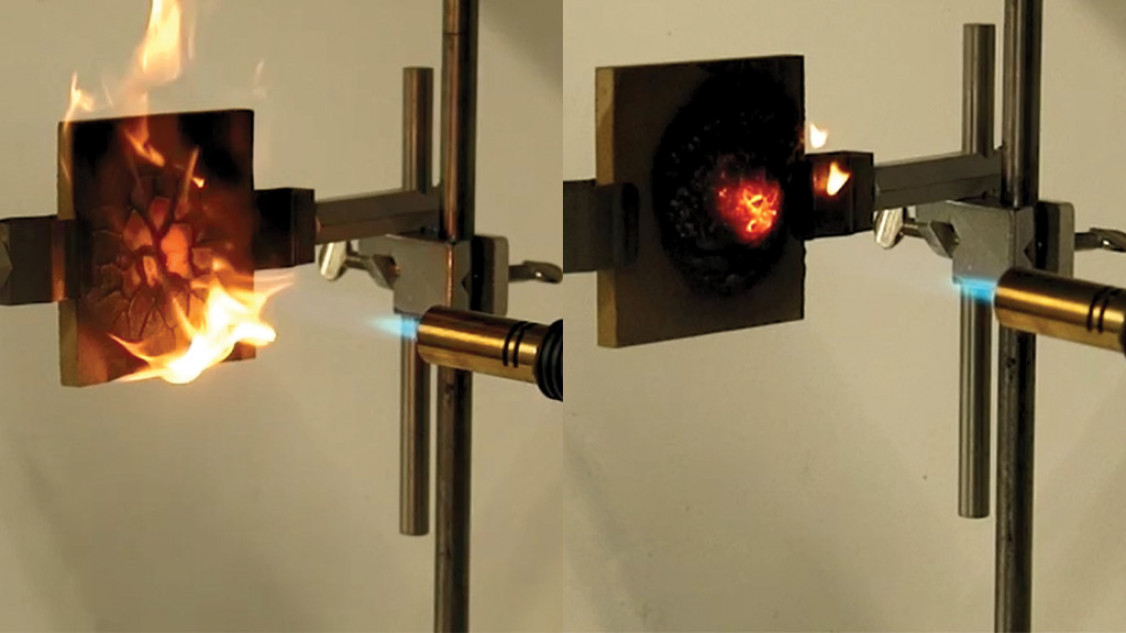
Recycling epoxy resins is anything but trivial, because these plastics are so-called thermosets. In this type of polymer, the polymer chains are closely crosslinked. These chemical crosslinks make melting impossible. Once the plastic has hardened, it can no longer be reshaped.
This is not the case for thermoplasts, such as PET or polyolefins. Their polymer chains lie close together but are not chemically linked to each other. When heated, these polymers can be melted and formed into new shapes. However, because of the lack of crosslinks, their mechanical properties at elevated temperatures are generally not as good as those of thermosets.
A new kind of polymer
The unique epoxy resin that the Empa researchers have developed in collaboration with national and international partners is technically a thermoset – but unlike other thermosets, it can be reshaped like a thermoplast. The key is the addition of a very special functional molecule from the class of phosphonate esters into the new resin matrix. “We originally synthesized this molecule as a flame retardant,” says co-inventor of this technology and Empa scientist Wenyu Wu Klingler. However, the bond the molecule forms with the polymer chains of the epoxy resin is dynamic and can be broken under certain conditions. This loosens the crosslinking of the polymer chains so that they can be melted and reshaped.
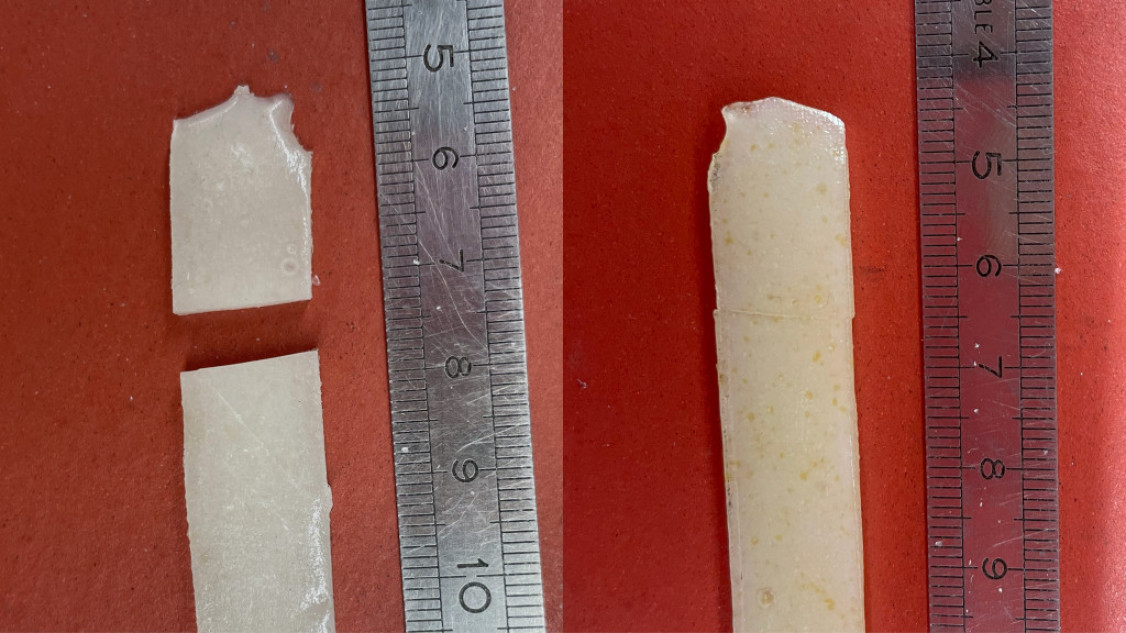

Such materials, also known as vitrimers, have only been known for about ten years and are considered particularly promising. “Today, fiber-reinforced composites are not recyclable at all, except under very harsh conditions, which damage the recovered fibers,” explains Wu Klingler. “Once they have reached the end of their service life, they are incinerated or disposed of in landfills. With our plastic, it would be possible for the first time to bring them back into circulation again.”
“Our vision for the future,” adds group leader Sabyasachi Gaan, “is a composite material, in which both the fibers and the plastic matrix can be completely separated and reused.” The researcher sees an opportunity in carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics in particular, as they're commonly used in the construction of airplanes, trains, boats, cars, bicycles and more. “The production of carbon fibers requires a lot of energy and releases an enormous amount of CO2,” he explains. “If we could recycle them, their environmental footprint would be a lot better – and the price a lot lower.” Moreover, the recovery of valuable elements like phosphorus connected to the matrix polymer would be possible.
A material made to measure
Fiber-reinforced composites are not the only application for the new polymer. For example, it could be used to coat wooden floors, as a transparent, resistant layer that has good flame-retardant properties – and where scratches and dents can be “healed” with a little pressure and heat.
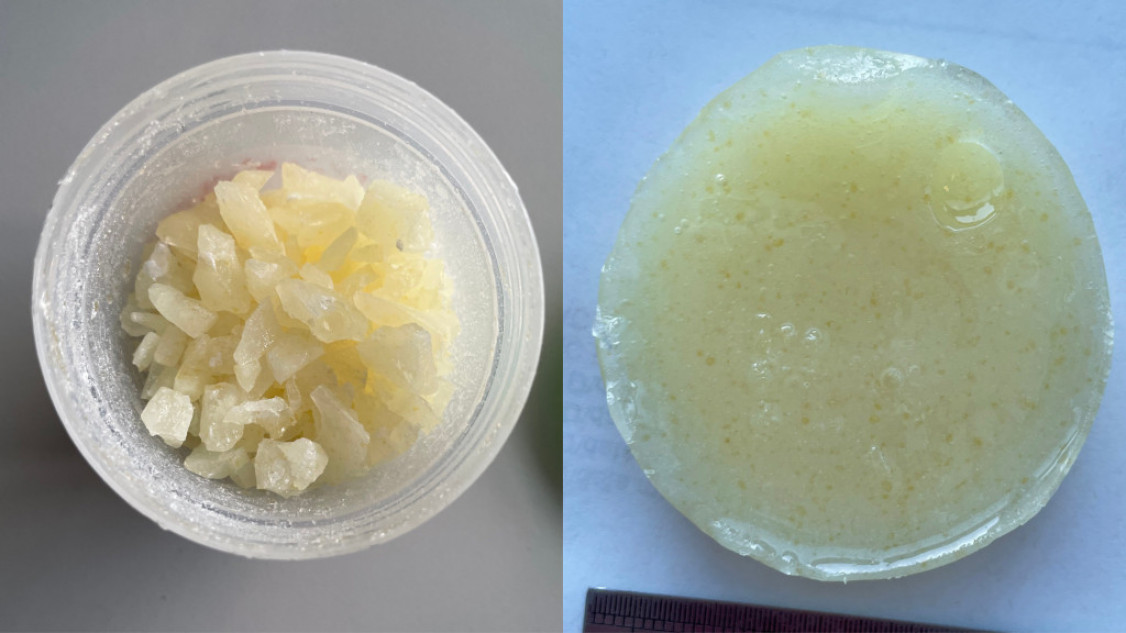
“We didn't develop a single material for a specific purpose, but rather a toolbox,” Gaan explains. “Flame retardancy, recyclability and repairability are a given. We can optimize all other properties depending on the intended use.” For example, he says, flow characteristics are particularly important for the production of fiber-reinforced plastics, while exterior wood coatings should also be weather-resistant.
To pursue these and other applications of the material, the researchers are now looking for industrial partners. The chances of commercial success are good: In addition to all its other advantageous properties, the modified epoxy polymer is also inexpensive and easy to manufacture.
European Meeting on Fire Retardant Polymeric Materials 2023
Empa's Advanced Fibers laboratory, of which Sabyasachi Gaan and Wenyu Wu Klingler are members, has been developing flame retardants for textiles, plastics and wood for 15 years. On July 26-29, the lab successfully hosted the European Meeting on Fire Retardant Polymeric Materials (FRPM) 2023 at the Empa Academy, bringing together 250 experts from academia and industry for interdisciplinary presentations and discussions. This project was also presented at the conference.
Literature:
(Source: Empa, Author: Anna Ettlin)






