Those who regard process gases for welding as an integral component of the automated welding system increase both process reliability and seam quality. At the same time, post-processing effort is reduced – along with emissions generated during the process. With a holistic approach, productivity, sustainability and competitiveness can be permanently improved. The automation of welding technology continues to advance. Robots, cobots and networked production cells are increasingly finding their way into industrial manufacturing – whether in the automotive industry, mechanical engineering or highly specialized sectors such as aerospace and medical technology. As a result, the demands on welding processes are also rising significantly: they must be reproducible to ensure consistently high quality, low in emissions to meet environmental and occupational safety standards and flexibly controllable to economically handle small batch sizes and varying component designs.
Especially in industries such as aerospace or medical technology, where the highest safety and quality standards apply, process stability must not fluctuate. Often, the smallest weld seam can determine the functionality and service life of a component. At the same time, pressure is increasing to reduce the environmental impact of welding fumes and emissions – both to comply with legal requirements and to protect employees.
Medium-sized companies and small-batch manufacturers in particular face challenges. While large companies with the right equipment often rely on extensive automation and process control, smaller firms must remain flexible with limited resources – for example, when producing changing component variants or meeting tight delivery deadlines. Here, sensor technology is gaining importance: precise measuring and monitoring systems detect process deviations in real time and enable rapid adjustments. Equally indispensable is consistent quality assurance to avoid rejects and minimize rework. At the same time, occupational safety is becoming more and more of a priority, especially in automated environments where humans and machines work closely together.
Shielding gases as a solution to current challenges
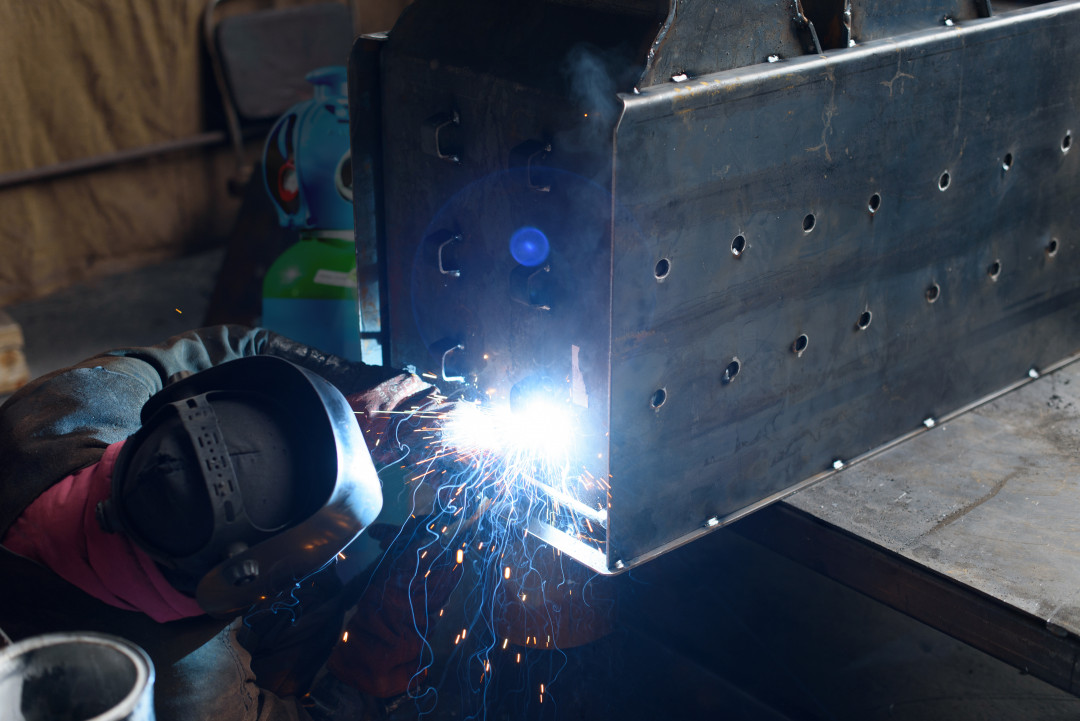
Amidst these challenges, one factor is moving into focus that is often underestimated: shielding gas. Shielding gases surround the weld zone with a controlled atmosphere that protects against environmental influences, stabilizes the arc, and optimizes metal transfer (Fig. 1). Especially in automated processes, the targeted selection and precise dosing of shielding gases is a decisive factor for consistent welding quality and process stability.
Historically, the use of shielding gases in welding technology has advanced considerably. While simple argon or CO₂ gases were used in the past, modern gas mixtures today enable finely tuned process control. They reduce spatter, prevent pore formation, and lower emissions. This offers significant advantages, particularly in automated production, where processes are repeated hundreds or thousands of times. Shielding gas thus becomes an invisible but indispensable component in production, contributing decisively to quality, efficiency, and environmental sustainability.
Shielding gases ensure process stability
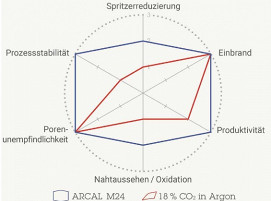
Automated welding processes require constant and stable workflows. Fluctuations in the arc or uncontrolled droplet transfer impair weld seam quality, leading to uneven welds or even rejects. Welding process gases such as Arcal 14, Arcal M24 and Teral 24-7 from Air Liquide stabilize the arc, control droplet formation and improve seam quality. They ensure a calm, stable arc that enables uniform and clean welds (Fig. 2).
Depending on the working environment and welding technique, different requirements are placed on the process gas. Robots usually work in enclosed welding cells, while cobots are often used in open or semi-open areas with direct human-machine collaboration. This places different demands on shielding gases. In addition to weld quality, workplace conditions and the reduction of welding fume emissions also play an important role. Arcal gases reduce spatter and welding fume emissions, improve air quality in the workplace, and lower the need for fume extraction—important factors especially for cobots in open production environments.
Special gas solutions for different applications
Each welding task places specific demands on the shielding gas. Air Liquide therefore offers a broad portfolio of customized gas solutions for automated welding:
- Arcal 14: This shielding gas produces a fine-scaled seam with very low spatter formation. It is well-suited for welding in all positions and is particularly advantageous for automated welding processes, such as with cobots, which often perform welds in visible areas.
- Teral 24-7: Designed specifically for medium sheet thicknesses, as commonly found in commercial vehicles, agricultural machinery, or mechanical engineering. The gas reduces fumes, slag, and rework, making it highly suitable for series production with cobots, where short cycle times and high process reliability are required.
- Arcal M24: Developed for both manual and automated welding processes. It offers deep penetration, low porosity, and high weld seam reliability.
Process reliability requires system understanding
Automated welding processes demand more than just technology. They require an understanding of the interactions between workpiece, process, and medium. The shielding gas used plays an invisible yet central role in seam quality, stability and the amount of post-processing required. Those who systematically select their gases and integrate them into process planning can avoid sources of error and significantly increase equipment availability.
What clean weld seams achieve
The quality of the weld seam is critical to the function and economic efficiency of automated production processes. Defects such as spatter, silicate deposits or uneven weld seams not only impair appearance but also compromise the dynamic strength of components. In addition, such defects can interfere with traceability (sensor systems), leading to rejects, rework and lost time. Arcal welding process gases specifically minimize these errors by using tailored active gas components to control droplet formation and stabilize the arc – thus ensuring consistent results.
Consistent seam quality with reduced rework
Especially with components that have sensitive galvanic coatings or paint finishes, low-activity shielding gases show clear advantages: they produce slag-free, smooth seams without residues that could damage the surface. In addition, Arcal gases can reduce silicate formation. This lowers scrap rates, protects subsequent processes and is particularly beneficial in cobot welding for visible seams or thin-walled components.
Workplace safety and working conditions
In addition to welding process quality, workplace safety and conditions are becoming increasingly important – not only out of responsibility toward employees, but also due to legal requirements and sustainability goals. Arcal gases reduce welding fume emissions and particles. Lowering these emissions improves air quality, reduces strain on employees, decreases cleaning effort and makes it easier to comply with legal limits. Companies benefit from reduced downtime, lower operating costs, and an improved sustainability record. Thus, process gases strengthen not only quality but the entire production process—technically as well as economically.
Application determines efficiency
The choice of the right process gas is crucial – but so is its precise application in the specific process. To fully exploit the potential of gases, they should be exactly matched to the components, welding position and method. Regular process checks help detect fluctuations early. Air Liquide supports users with technical consulting and tailored services – from gas selection to integration of gases into the production line.
Users should also always monitor the quality of the gases they use. Deviations must be documented and parameters systematically tracked. Only in this way can sources of error be quickly identified. Continuous training in the handling of gases and system technology also ensures the transfer of expertise within production.
(Source: Norbert Semsch, Expert for Welding and Cutting Gases, Air Liquide Deutschland GmbH)
Schlagworte
AerospaceApplicationAutomationAutomotiveCobotsEVGasIndustryManufactureOccupational SafetyProductionRobotsSafetyShielding GasesWeldWeld SeamWeldingWelding TechnologyWorkplaceWorkplace Safety